IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNINGS:
SERIOUS INFECTIONS, MORTALITY, MALIGNANCY, MAJOR ADVERSE CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS, AND THROMBOSIS
SERIOUS INFECTIONS - Patients treated with Olumiant are at risk for developing serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death. Most patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids. If a serious infection develops, interrupt Olumiant until the infection is controlled. Reported infections include:
- Active tuberculosis (TB), which may present with pulmonary or extrapulmonary disease. Olumiant should not be given to patients with active tuberculosis. Test patients, except those with COVID-19, for latent TB before initiating Olumiant and during therapy. If positive, start treatment for latent infection prior to Olumiant use.
- Invasive fungal infections, including candidiasis and pneumocystosis. Patients with invasive fungal infections may present with disseminated, rather than localized, disease.
- Bacterial, viral, and other infections due to opportunistic pathogens.
Carefully consider the risks and benefits of Olumiant prior to initiating therapy in patients with chronic or recurrent infection.
Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with Olumiant including the possible development of TB in patients who tested negative for latent TB infection prior to initiating therapy.
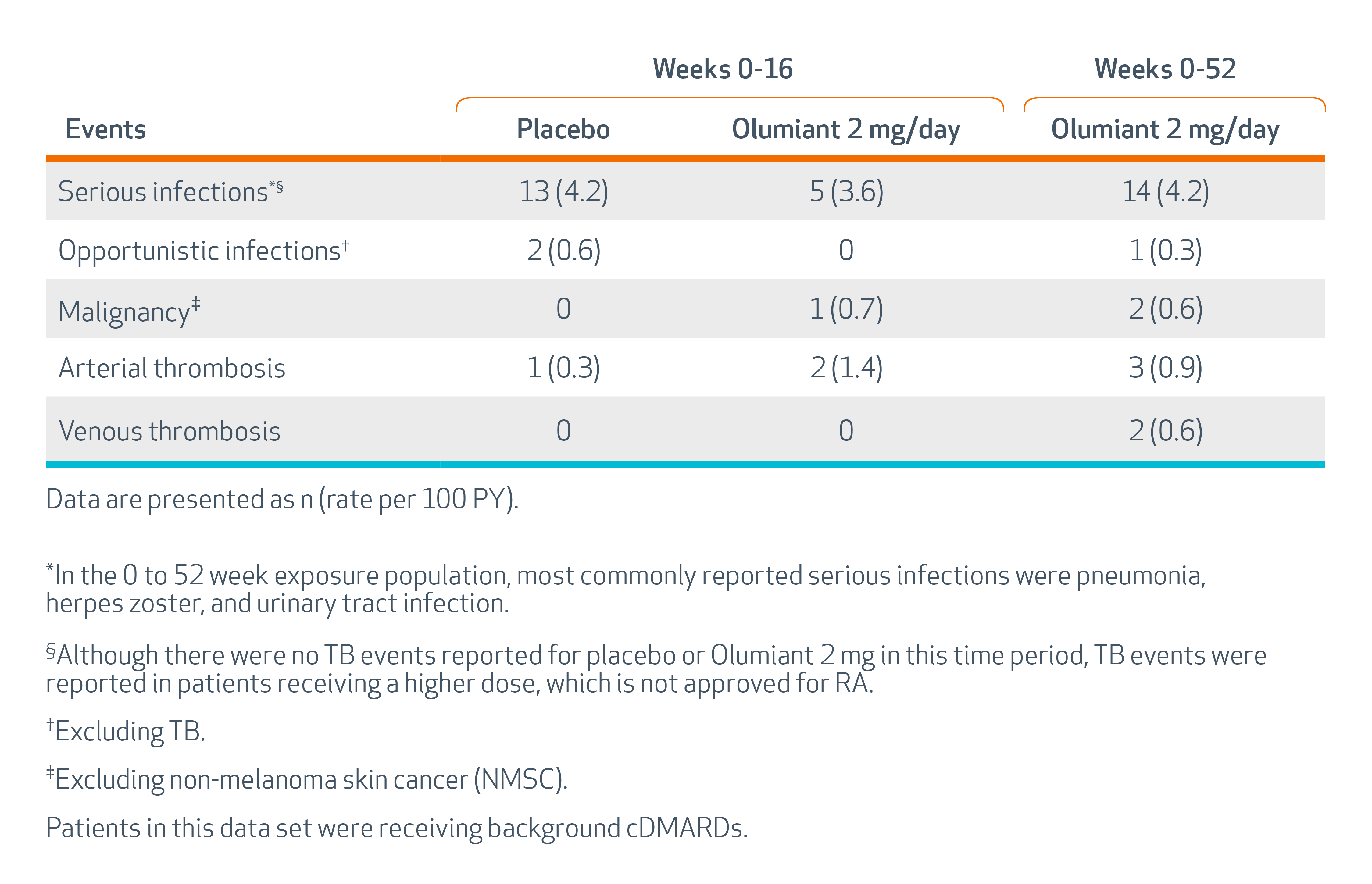
The most common serious infections reported with Olumiant included pneumonia, herpes zoster, and urinary tract infection. Among opportunistic infections, tuberculosis, multidermatomal herpes zoster, esophageal candidiasis, pneumocystosis, acute histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis, cytomegalovirus, and BK virus were reported with Olumiant. Some patients have presented with disseminated rather than localized disease, and were often taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids.
Avoid use of Olumiant in patients with an active, serious infection, including localized infections. Consider the risks and benefits of treatment prior to initiating Olumiant in patients: with chronic or recurrent infection; who have been exposed to TB; with a history of a serious or an opportunistic infection; who have resided or traveled in areas of endemic tuberculosis or endemic mycoses; or with underlying conditions that may predispose them to infection.
The risks and benefits of treatment with Olumiant in COVID-19 patients with other concurrent infections should be considered.
Consider anti-TB therapy prior to initiation of Olumiant in patients with a history of latent or active TB in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed, and for patients with a negative test for latent TB but who have risk factors for TB infection.
Viral reactivation, including cases of herpes virus reactivation (e.g., herpes zoster), were reported in clinical studies with Olumiant. If a patient develops herpes zoster, interrupt Olumiant treatment until the episode resolves. The impact of Olumiant on chronic viral hepatitis reactivation is unknown. Screen for viral hepatitis in accordance with clinical guidelines before initiating Olumiant.
MORTALITY
In a large, randomized, postmarketing safety study in RA patients 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor comparing another Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockers, a higher rate of all-cause mortality, including sudden cardiovascular death, was observed with the JAK inhibitor.
Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with Olumiant.
MALIGNANCIES
Lymphoma and other malignancies have been observed in patients treated with Olumiant. In RA patients treated with another JAK inhibitor, a higher rate of malignancies (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer [NMSC]) was observed when compared with TNF blockers. Patients who are current or past smokers are at additional increased risk.A higher rate of lymphomas was observed in patients treated with the JAK inhibitor compared to those treated with TNF blockers. A higher rate of lung cancers and an additional increased risk of overall malignancies were observed in current or past smokers treated with the JAK inhibitor compared to those treated with TNF blockers.
Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with Olumiant, particularly in patients with a known malignancy (other than successfully treated NMSC), patients who develop a malignancy, and patients who are current or past smokers.
NMSCs have been reported in patients treated with Olumiant. Periodic skin examination is recommended for patients who are at increased risk for skin cancer.
MAJOR ADVERSE CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
In RA patients 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor treated with another JAK inhibitor, a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) (defined as cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction [MI], and stroke) was observed when compared with TNF blockers. Patients who are current or past smokers are at additional increased risk. Discontinue Olumiant in patients that have experienced a myocardial infarction or stroke.
Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with Olumiant, particularly in patients who are current or past smokers and patients with other cardiovascular risk factors. Inform patients about the symptoms of serious cardiovascular events and the steps to take if they occur.
THROMBOSIS
Thrombosis, including deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), has been observed at an increased incidence in patients treated with Olumiant compared to placebo. In addition, there were cases of arterial thrombosis. Many of these adverse events were serious and some resulted in death. In RA patients 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor treated with another JAK inhibitor, a higher rate of thrombosis was observed when compared with TNF blockers. Avoid Olumiant in patients at risk. Discontinue Olumiant and promptly evaluate patients with symptoms of thrombosis.
HYPERSENSITIVITY
Reactions such as angioedema, urticaria, and rash that may reflect drug hypersensitivity have been observed in patients receiving Olumiant, including serious reactions. If a serious hypersensitivity reaction occurs, promptly discontinue Olumiant while evaluating the potential causes of the reaction.
GASTROINTESTINAL PERFORATIONS
Gastrointestinal perforations have been reported in Olumiant clinical studies. Monitor Olumiant-treated patients who may be at increased risk for gastrointestinal perforation (e.g., patients with a history of diverticulitis). Promptly evaluate patients who present with new onset abdominal symptoms for early identification of gastrointestinal perforation.
LABORATORY ABNORMALITIES
Neutropenia – Olumiant treatment was associated with an increased incidence of neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count [ANC] <1000 cells/mm3) compared to placebo. Evaluate at baseline and thereafter according to routine patient management.
In patients with RA or alopecia areata (AA), avoid initiation or interrupt Olumiant treatment in patients with an ANC <1000 cells/mm3. In patients with COVID-19, avoid initiation or interrupt Olumiant treatment in patients with an ANC <500 cells/mm3.
Lymphopenia – Absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) <500 cells/mm3 were reported in Olumiant clinical trials. Lymphocyte counts less than the lower limit of normal were associated with infection in patients treated with Olumiant, but not placebo. Evaluate at baseline and thereafter according to routine patient management.
In patients with RA or AA, avoid initiation or interrupt Olumiant treatment in patients with an ALC <500 cells/mm3. In patients with COVID-19, avoid initiation or interrupt Olumiant treatment in patients with an ALC <200 cells/mm3.
Anemia – Decreases in hemoglobin levels to <8 g/dL were reported in Olumiant clinical trials. Evaluate at baseline and thereafter according to routine patient management.
In patients with RA or AA, avoid initiation or interrupt Olumiant treatment in patients with hemoglobin <8 g/dL. In patients with COVID-19, there is limited information regarding use of Olumiant in patients with hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL.
Liver Enzyme Elevations – Olumiant treatment was associated with increased incidence of liver enzyme elevation compared to placebo. Increases of alanine transaminase (ALT) ≥5x upper limit of normal (ULN) and increases of aspartate transaminase (AST) ≥10x ULN were observed in patients in Olumiant clinical trials.
Evaluate at baseline and thereafter according to routine patient management. Promptly investigate the cause of liver enzyme elevation to identify potential cases of drug-induced liver injury. If increases in ALT or AST are observed and drug-induced liver injury is suspected, interrupt Olumiant until this diagnosis is excluded.
Lipid Elevations – Treatment with Olumiant was associated with increases in lipid parameters, including total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Assess lipid parameters approximately 12 weeks following Olumiant initiation in patients with RA or AA. Manage patients according to clinical guidelines for the management of hyperlipidemia.
VACCINATIONS
Avoid use of live vaccines with Olumiant. Update immunizations in patients with RA or AA prior to initiating Olumiant therapy in agreement with current immunization guidelines.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
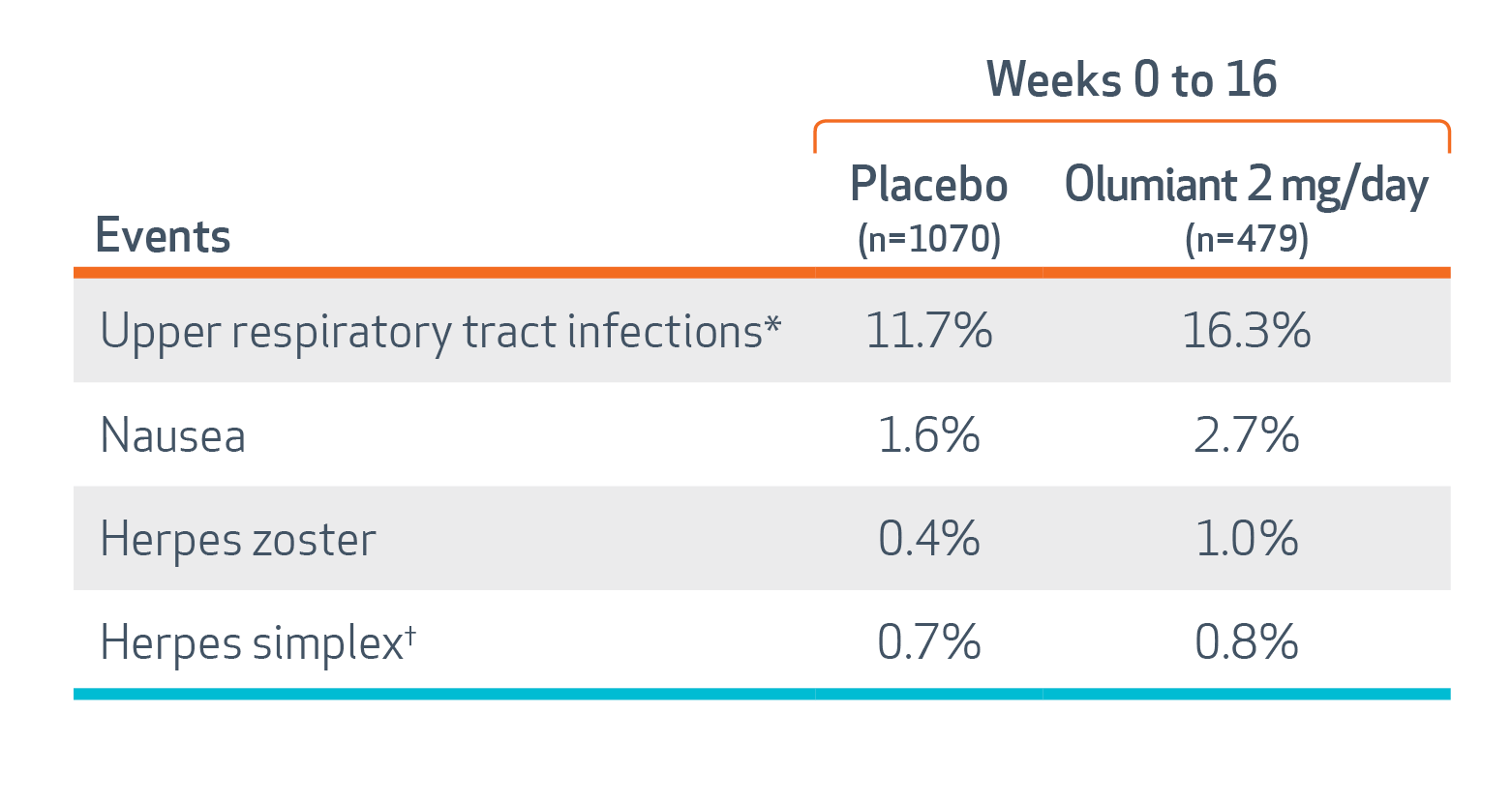
In RA trials, the most common adverse reactions (≥1%) reported with Olumiant were: upper respiratory tract infections, nausea, herpes simplex, and herpes zoster.
In COVID-19 trials, the most common adverse reactions (≥1%) reported with Olumiant were: ALT ≥3x ULN, AST ≥3x ULN, thrombocytosis (platelets >600,000 cells/mm3), creatine phosphokinase >5x ULN, neutropenia (ANC <1000 cells/mm3), DVT, PE, and urinary tract infection.
In AA trials, the most common adverse reactions (≥1%) reported with Olumiant were: upper respiratory tract infections, headache, acne, hyperlipidemia, creatine phosphokinase increase, urinary tract infections, liver enzyme elevations, folliculitis, fatigue, lower respiratory tract infections, nausea, genital Candida infections, anemia, neutropenia, abdominal pain, herpes zoster, and weight increase.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION
Based on animal studies, Olumiant may cause fetal harm when administered during pregnancy. Advise pregnant women and women of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Consider pregnancy planning and prevention for women of reproductive potential. Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with Olumiant and for 4 days after the last dose.
HEPATIC AND RENAL IMPAIRMENT
Olumiant is not recommended in patients with RA or AA and severe hepatic impairment or severe renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] <30 mL/min/1.73m2).
Olumiant should only be used in patients with COVID-19 and severe hepatic impairment if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk. Olumiant is not recommended in patients with COVID-19 who are on dialysis, have end-stage renal disease, or with eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73m2.
BA HCP ISI ALL 14SEP2022
Please click to access full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning about Serious Infections, Mortality, Malignancy, Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events, and Thrombosis, and Medication Guide.